What do we analyze?
We analyze addresses for belonging to more than 20 sources of risk to find suspicious transactions and determine the risk factor. We divided all sources into three categories.
✋Be Careful!
The presence of Dark Market, Dark Service, Illegal Service is a bad sign.
We recommend carrying out additional investigations in order not to lose your funds due to blocking.
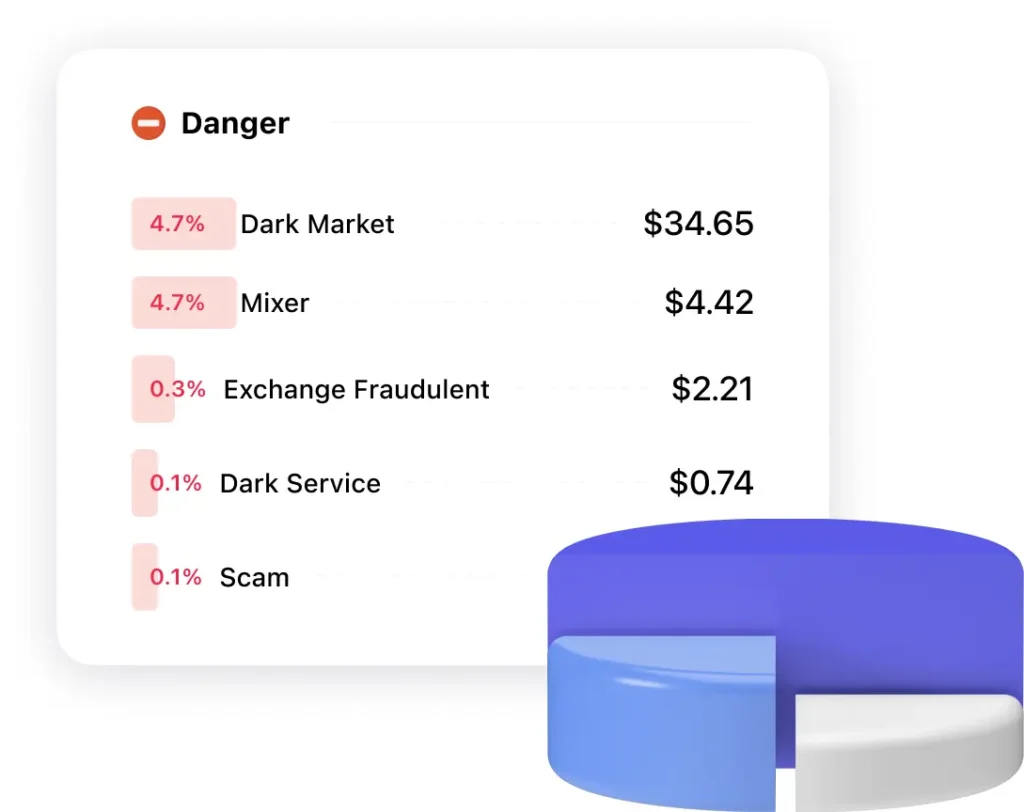
Danger
Child Exploitation
Persons associated with child exploitation.
Dark Market
Coins associated with illegal activities.
Dark Service
Coins related to child abuse, terrorist financing or drug trafficking.
Enforcement action
The entity is subject to proceedings with legal authorities.
Fraud Shop
An entity that sells various types of data, including personal information, credit card information, and stolen accounts.
Fraudulent transactions usually differ from darknet markets in their behavior, such as constant replenishment of deposits and no incoming transactions to customers.Fraudulent Exchange
Exchanges involved in exit scams, illegal behavior, or whose funds have been confiscated by government authorities.
Gambling
Coins associated with unlicensed online games
High-Risk Jurisdiction
The jurisdiction that is listed on the the FATF’s non-cooperative list, has extensive malicious cryptocurrency activity or lacks a sophisticated regulatory environment.
Including countries such as Iran, Venezuela, Albania and Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, also known as North Korea.Illegal Service
Coins associated with illegal activities.
Illicit Actor/Organization
An organization or physical person who directly or indirectly participates in various forms of illegal activity.
It is often associated with such risky topics as darknet markets, fraudulent transactions, extremist financing and hacking.Mixer
Coins that passed through a mixer to make tracking difficult or impossible. Mixers are mainly used for money laundering.
Online Pharmacy
Entities specializing in the illicit sale of unapproved or prescription medication. Comparable to darknet markets, but may operate on both dark and clear web, warranting a separate classification
Ransom
Coins obtained through extortion or blackmail.
Sanctions
Sanctioned entities.
Scam
Coins that were obtained by deception.
Special Measures
Entities or addresses identified by FinCEN as being of “primary money laundering concern”. Countermeasures include recordkeeping, reporting requirements, and restrictions on fund transfers and account management.
The scope may extend to similar authorities in other countries or jurisdictions as they are implemented.Stolen Coins
Coins obtained by hijacking someone else’s cryptocurrency.
Terrorism Financing
Suspicious sources
ATM
Coins obtained via cryptocurrency ATM operator.
DEX
The blockchain application that facilitates cryptocurrency and token trading through automated smart contracts.
Trades on the decentralized platform are peer-to-peer and have no third party or central authority other than the smart contract that executes the trades, making it a popular money laundering tool among malicious actors.Exchange | High Risk
An entity becomes high-risk based on the following criteria:
No KYC: Requires absolutely no customer information before allowing any level of deposit/withdrawal, or makes no attempt to verify that information.
Criminal Connections: Criminal charges against the legal entity in connection with AML/CFT violations.
Impact: High exposure to risky services such as darknet markets, other high-risk exchanges, or blending is defined as a service whose direct high-risk exposure differs by one standard deviation from the average of all identified exchanges over a 12-month period.
Jurisdiction: based in a jurisdiction with weak AML/CFT measures.
Unlicensed: Does not have any specific license to trade cryptocurrencies.Infrastructure as a Service
The organization that offers computing and information services, including but not limited to VPNs, VPS and domain registrations.
It could potentially represent a payment to privacy-focused providers that could be used for illicit purposes, but at the same time could represent a payment to completely legitimate business provider.Lending Contract
The blockchain application that allows users to peer-to-peer lend and borrow crypto assets peer-to-peer without interacting with a third party or central authority.
Liquidity Pools
Smart contracts where tokens are locked up to provide liquidity.
P2P Exchange | High Risk
The organization does not have any special license to conduct business related to the provision of cryptocurrency exchange services, when participants exchange directly with each other, without intermediaries.
It also includes entities that are licensed but located in listed jurisdictions, are listed as non-cooperating companies by the FATF, or do not provide KYC for large-value transactions, making them attractive for money laundering.Privacy Protocol
A protocol or entity that uses privacy features, such as zero-knowledge proofs, to provide users with privacy features.
Ensuring transparency of transactions, but at the same time, the addresses of counterparties remain hidden.
This feature is the default behavior of many privacy-protecting cryptocurrencies such as Monero and Secret, meaning that gaining access to these assets does not necessarily mean that funds have been mixed or deliberately obfuscated.Smart Contract
Blockchain functionality that functions like a self-executing contract, with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller written directly into lines of code, executable without the need for a third party.
Token Smart Contract
The crypto asset that is built on another blockchain and that can be sent and received using a crypto wallet.
There are various technical standards of agreed rules that guide the design, development, behaviour and operation of the given token.Unnamed Service
The category refers to currently unidentified clusters that exhibit the behavior expected of a service, by a large number of addresses and transactions.
Trusted sources
Exchange
The organization allows users to buy, sell and trade cryptocurrencies by holding trading licenses that include the following aspects of the services:
— Depository, brokerage or other related financial services that provide exchange services where participants interact with a central party.
And does not include:
— Licenses for non-specific financial services and jurisdictions included in the FATF non-cooperative list.
They represent the most important and most used category of entities in the cryptocurrency industry, accounting for 90% of all funds sent through these services.ICO
The organization that crowdfunds its project by selling their newly minted cryptocurrency to investors in exchange for fiat currency or more common cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ether.
There are many legitimate examples of these offerings, but also many cases where bad actors raise funds through ICOs, then they take the money and disappear.Marketplace
Coins that were used to pay for legal activities
Merchant Services
The entity that allows businesses to accept payments from their customers, also known as payment gateways or payment processors.
It often faciliates conversions to local fiat currency and clearing the funds into the merchant’s bank account.Miner
Coins mined by miners and not forwarded yet.
Other
Coins obtained through airdrops, token sales or other means.
P2P Exchange
The entity is licensed to conduct a business that is specific to providing cryptocurrency exchange services where participants exchange directly with each other, without a middleman.
It does not include non-specific financial services licenses and jurisdictions that are on the non-cooperative FATF list.Payment Processor
Coins associated with payment services.
Seized Assets
Crypto assets seized by the government.
Wallet
Coins stored in verified wallets.